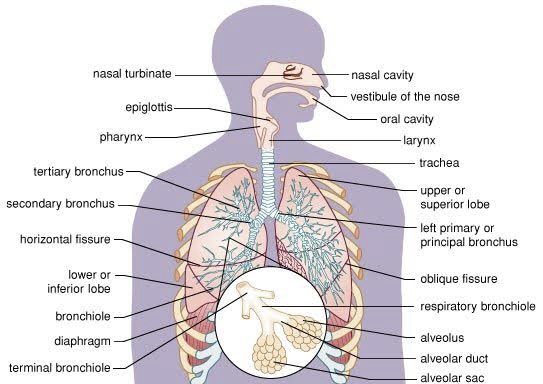
Respiratory system is composed of following organs –
Human respiratory system-
- Nasal cavity
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Right and left principle bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Lungs
Larynx or voice box
The larynx is the organ for production of voice . It is also an air passage and acts as a sphincter at the inlet of lower respiratory passage.
The upper respiratory passage include the nose, the nasopharynx and the oropharynx.
Situation
- The larynx lies in the anterior midline of the neck.
- The larynx is a short passage that connects the laryngopharynx (root of the tongue) to the trachea.
- It lies in front of C3-C4
Measurement
Length – 44 mm in male.
36 mm in female
- At puberty male larynx grows rapidly and become larger than the female larynx.
- The pubertal growth of female larynx is negligible.
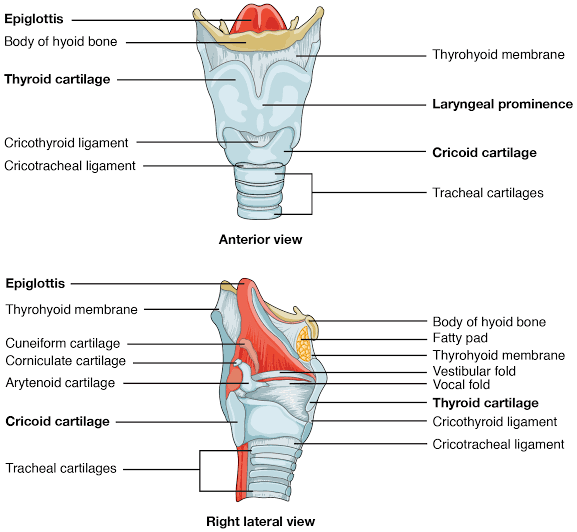
Constitution of larynx-
The larynx is made up of a skeletal framework of cartilages. The cartilage are connected by joints, ligaments and membranes and are moved by a number of muscles. The cavity of the larynx is lined by mucous membrane.
Skeleton of larynx-
The wall of larynx consists of 9 pieces of cartilage out of which three are unpaired and three are paired.
- Unpaired cartilage
- Thyroid cartilage / Adam’s apple- The thyroid cartilage consists of two fused plates of hyaline cartilage that form the anterior wall of the larynx and give it triangular shape. It is usually larger in males than females due to the influence of male sex hormones during puberty. This gives ‘V’ shape in cross section and the ligament connecting the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone is known as thyrohoid membrane.
- Cricoid cartilage- Ring shape
- Epiglottic cartilage- Leaf shape
- Paired cartilage
- Arytenoid cartilage-Two small cartilages that have pyramid shape and are most important since they influence the position and tensions of the vocal cord.
- Corniculate cartilage- They are two, small vocal nodules .
- Cuneiform cartilage – They are two, small having rod like shape.
Laryngeal joints –
There are two laryngeal joints-
- Cricothyroid joints
- Cricoarytenoid joints
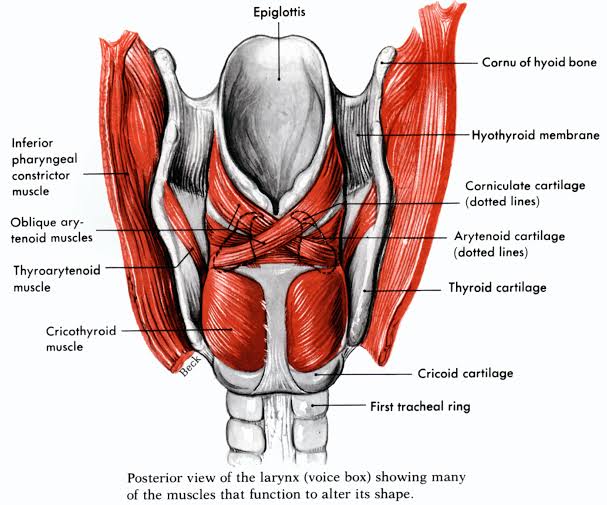
Intrinsic muscles of larynx-
| Muscles – Nerve supply | |||
| Posterior cricoarytenoid – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Lateral cricoarytenoid – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Transverse arytenoid – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Oblique arytenoid – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Thyroarytenoid – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Thyroepiglotticus – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Aryepiglotticus – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Vocalis – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |||
| Cricothyroid – External laryngeal nerve |
Arterial supply-
Superior and inferior laryngeal artery supplies larynx .
Venous drainage –
Superior and inferior laryngeal vein supplies larynx.
Lymphatic drainage-
- Deep cervical nodes
- Prelaryngeal nodes
Nerve supply-
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Applied aspect-
- Laryngitis – Infection or inflammation of larynx is called laryngitis . It is characterised by hoarseness of voice.
- Laryngeal oedema – Obstruction to breathing.
- Laryngoscopy- Examination of larynx.
