FLAIL CHEST
- It occurs when two or more adjacent ribs are segmentally fractured in two or more places.
- There is hypoventilation (carbon dioxide retention and respiratory failure)
Treatment :-
- Pulmonary toilet : exercises and procedures that help to clear your airways of mucus and other secretions.
- Tube thoracostomy : insertion of a thin plastic tube into the pleural space (the area between the chest wall and lungs.)
- The tube is attached to a suction device to remove excess fluid or air.
PECTUS EXCAVATUM (FUNNEL CHEST OR SAUCER CHEST)
- The body of sternum, usually the lower end is curved backwards.
- The heart is displaced to the left and may be compresssed between the sternum and the vertebral column.
PECTUS CARINATUM (PIGEON CHEST)
- This is a malformation of the chest characterized by a protrusion of the sternum and ribs.
- It is usually caused by rickets and severe bronchial asthma in childhood.
PNEUMOTHORAX
- An abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the pleura.
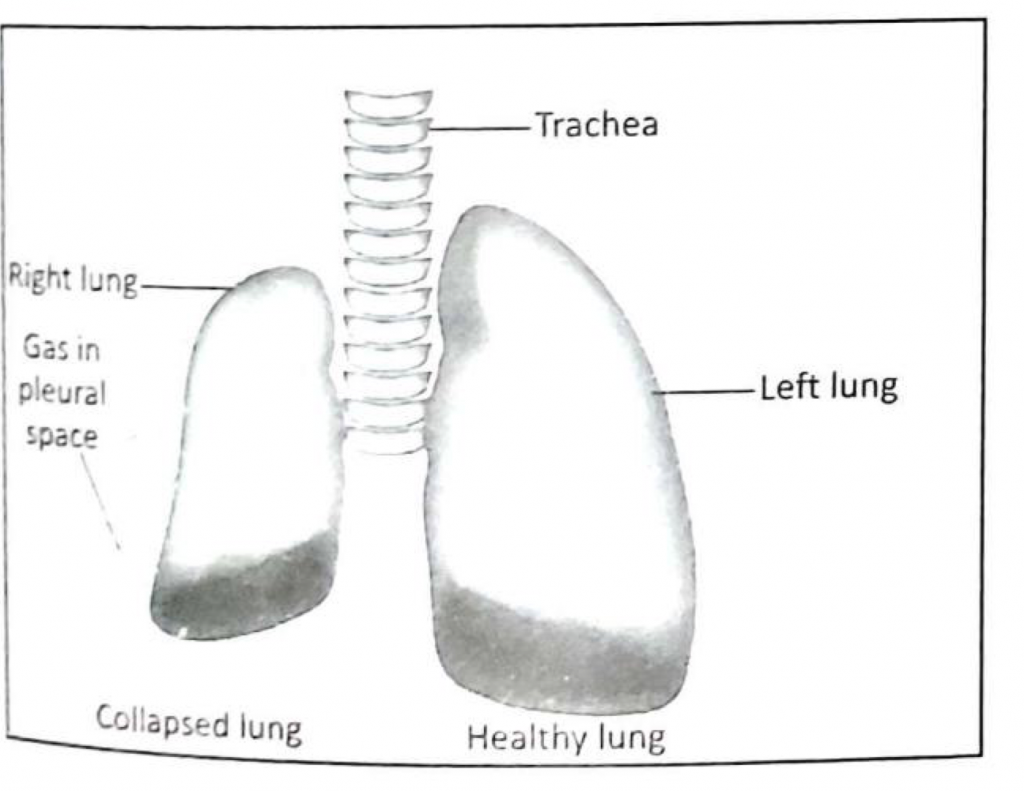
Classification :-
- Simple pneumothorax
- Open pneumothorax
- Tension pneumothorax
Simple pneumothorax :-
- It resolve without treatment and requires only monitoring.
Open pneumothorax :-
- Generally occurs due to penetrating thoracic trauma when the chest wall wound remains patent.
- Treatment : By closure of the wound, intercostal tube drainage (ICD) and surgery.
Tension pneumothorax :-
- It is an immediately life threatening injury that results when gas builds up under pressure within the pleural space after blunt or penetrating thoracic trauma.
- In this condition, respiratory gases may escape from the injured lung during each respiratory cycle or may be entrained into the pleural cavity from the outside during inspiration.
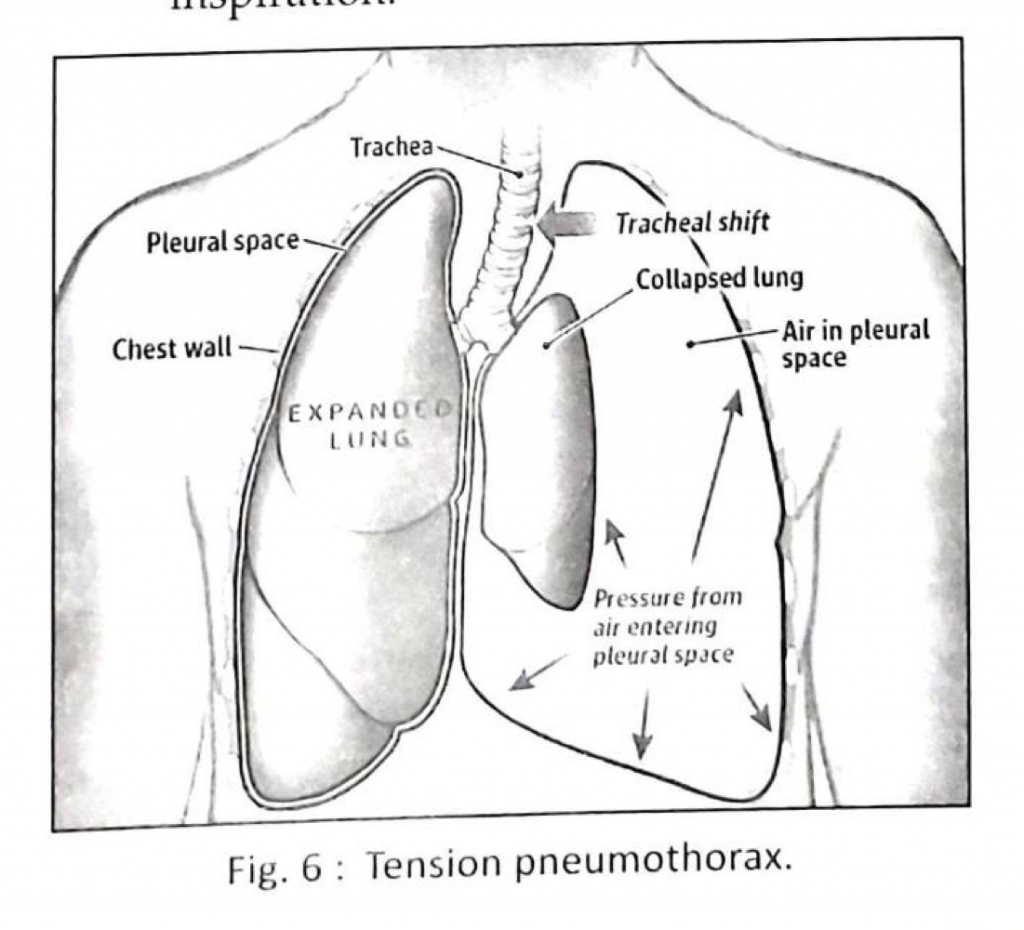
Treatment :-
Tension pneumothorax should be treated by prompt needle thoracostomy.
